Motivation
Wenn man Tabellen auf eine Webseite bringen will und diese etwas anspruchsvoller formatieren möchte, ist der Aufwand recht hoch.
Microsoft Excel ist ein mächtiges Programm und bietet schier unermäßliche Möglichkeiten.
Es nur naheliegend, Excel auch für die Erstellung und Formatierung der Tabellen zu benutzen, die ins WEB sollen…
Im Folgenden wird kurz beschrieben, wie mittels VBA von Excel eine Tabelle in HTML-Code umgesetzt werden kann.
Eine entsprechende Exportfunktion bietet Excel nicht. Excel kann wohl nach HTML exportieren. Aber dann wird eine komplette Webseite erstellt.
Wenn man nur eine Tabelle exportieren möchte, um das Ergebnis dann in den HTML-Code einer Webseite zu integrieren, kann der folgende VBA-Code verwendet werden.
Funktionsumfang – was die Konvertierung zurzeit leistet
- Formatierung der Zellen weitgehend übernehmen, aktuell umgesetzt für
- Schriftfarbe, Schriftart, Schriftstile und -größe
- Hintergrundfarbe
- Rahmenlinien: Farbe, Stile, Stärke
- Ausrichtung der Inhalte
- Verbundene Zellen vertikal und horizontal
- Zeilenhöhen
- Spaltenbreiten
- ausgeblendete Spalten und Zeilen sollen nicht übernommen werden
Einschränkung:
Bei Tabellen die als Tabelle formatiert sind (Tabellenformatvorlagen, Table styles) werden die Formateigenschaften nicht korrekt übernommen.
Endergebnis – das leistet das Makro zur Konvertierung
Hier der Bildschirmabzug einer formatierten Exceltabelle als Bild.
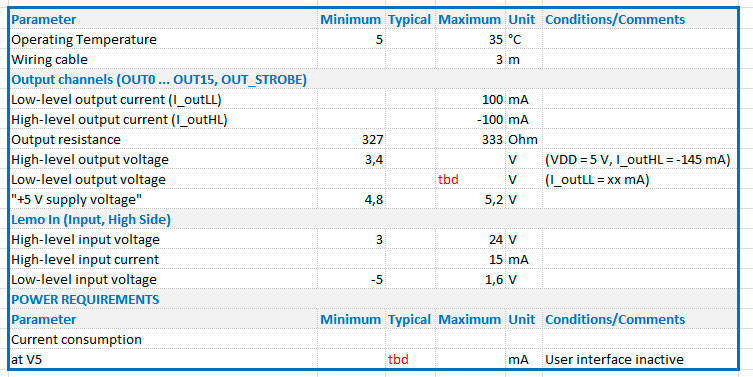
… und so erscheint die Tabelle als HTML-Code eingebunden, hier als (X)HTML-Version. Auf der Beispielseite als HTML5 mit „InBody“ (scoped) style sheet Excel-Tabelle als HTML- und CSS-Code eingebunden
| Parameter | Minimum | Typical | Maximum | Unit | Conditions/Comments |
| Operating Temperature | 5 | 35 | °C | ||
| Wiring cable | 3 | m | |||
| Output channels (OUT0 … OUT15, OUT_STROBE) | |||||
| Low-level output current (I_outLL) | 100 | mA | |||
| High-level output current (I_outHL) | -100 | mA | |||
| Output resistance | 327 | 333 | Ohm | ||
| High-level output voltage | 3,4 | V | (VDD = 5 V, I_outHL = -145 mA) | ||
| Low-level output voltage | tbd | V | (I_outLL = xx mA) | ||
| „+5 V supply voltage“ | 4,8 | 5,2 | V | ||
| Lemo In (Input, High Side) | |||||
| High-level input voltage | 3 | 24 | V | ||
| High-level input current | 15 | mA | |||
| Low-level input voltage | -5 | 1,6 | V | ||
| POWER REQUIREMENTS | |||||
| Parameter | Minimum | Typical | Maximum | Unit | Conditions/Comments |
| Current consumption | |||||
| at V5 | tbd | mA | User interface inactive | ||
Der erzeugte HTML-Code
Der Code besteht aus zwei Teilen. Einem Style-Sheet zur Einbindung in den body-Bereich (das ist nur ab HTML5 erlaubt) und einem HTML-Teil für die eigentliche Tabelle.
Der erzeugte HTML-Code für eine kleine Tabelle … Für HTML5-Seiten.
<table style="text-align: inherit; vertical-align: inherit;border-collapse: collapse;border-spacing: 0;width: inherit;border-color: #00B050 #000000 #00B050 #000000; border-style: solid none solid none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; "> <colgroup> <col width="80"> <col width="231"> </colgroup> <tbody> <tr style="height: 20px;"> <td class="tdc130037-0 tdc130037b-0" colspan="1" rowspan="1"> a</td> <td class="tdc130037-1 tdc130037b-0" colspan="1" rowspan="1"> b</td> </tr> <tr style="height: 20px;"> <td class="tdc130037-2 tdc130037b-1" colspan="1" rowspan="1"> a</td> <td class="tdc130037-3 tdc130037b-1" colspan="1" rowspan="1"> b</td> </tr> <tr style="height: 20px;"> <td class="tdc130037-4 tdc130037b-2" colspan="1" rowspan="1"> a</td> <td class="tdc130037-5 tdc130037b-2" colspan="1" rowspan="1"> b</td> </tr> </tbody> </table>
Das Style-Sheet mit den erzeugten CSS-Klassen zur Formatierung der Tabellen-Zellen. Ab HTML5 darf das style-Element im body-Bereich eingefügt werden. Weitere Informationen siehe hier.
Für Seiten, die mit Vorgängerversionen von HTML5 codiert sind, wird die Formatierung der Tabelle und der einzelnen Zellen über das style-Attribut realisiert. Siehe Beispiel-Code unten.
<style scoped>
td {
font-style: normal;
font-weight: normal;
font-size: 15px;
font-family: Calibri;
}
td.tdc130037b-0 {
border-color: #00B050 #000000 #000000 #000000;
border-style: solid none none none;
border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px;
}
td.tdc130037b-1 {
border-color: #000000 #000000 #000000 #000000;
border-style: none none none none;
border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px;
}
td.tdc130037b-2 {
border-color: #000000 #000000 #00B050 #000000;
border-style: none none solid none;
border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px;
}
td.tdc130037-0 {
color: #FF0000;
background-color: #A6A6A6;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
td.tdc130037-1 {
color: #000000;
background-color: #A6A6A6;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
td.tdc130037-2 {
color: #000000;
background-color: #FFFFFF;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
td.tdc130037-3 {
color: #E26B0A;
background-color: #FFFFFF;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
td.tdc130037-4 {
color: #963634;
background-color: #FFFFFF;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
td.tdc130037-5 {
color: #00B050;
background-color: #FFFFFF;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: bottom;
}
</style>
HTML-Code für die Verwendung in Seiten die Vorgängerversionen von HTML5 nutzen.
<table border='1' cellpadding='1' cellspacing='1' style="text-align: inherit; vertical-align: inherit;border-collapse: collapse;border-spacing: 0;width: inherit;border-color: #00B050 #000000 #00B050 #000000; border-style: solid none solid none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; "> <colgroup> <col width="80"> <col width="231"> </colgroup> <tbody> <tr> <td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="border-color: #00B050 #000000 #000000 #000000; border-style: solid none none none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; color: #FF0000;background-color: #A6A6A6;height: 20px;text-decoration: none; font-style: normal;font-weight: normal;font-size: 15px;font-family: Calibri;text-align: center;vertical-align: bottom;"> a</td> <td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="border-color: #00B050 #000000 #000000 #000000; border-style: solid none none none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; color: #000000;background-color: #A6A6A6;height: 20px;text-decoration: none; font-style: normal;font-weight: bold;font-size: 15px;font-family: Calibri;text-align: center;vertical-align: bottom;"> b</td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="border-color: #000000 #000000 #000000 #000000; border-style: none none none none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; color: #000000;background-color: #FFFFFF;height: 20px;text-decoration: none; font-style: normal;font-weight: normal;font-size: 15px;font-family: Calibri;text-align: center;vertical-align: bottom;"> a</td> <td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="border-color: #000000 #000000 #000000 #000000; border-style: none none none none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; color: #E26B0A;background-color: #FFFFFF;height: 20px;text-decoration: none; font-style: normal;font-weight: bold;font-size: 15px;font-family: Calibri;text-align: center;vertical-align: bottom;"> b</td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="border-color: #000000 #000000 #00B050 #000000; border-style: none none solid none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; color: #963634;background-color: #FFFFFF;height: 20px;text-decoration: none; font-style: normal;font-weight: normal;font-size: 15px;font-family: Calibri;text-align: center;vertical-align: bottom;"> a</td> <td colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="border-color: #000000 #000000 #00B050 #000000; border-style: none none solid none; border-width: 1px 1px 1px 1px; color: #00B050;background-color: #FFFFFF;height: 20px;text-decoration: none; font-style: normal;font-weight: bold;font-size: 15px;font-family: Calibri;text-align: center;vertical-align: bottom;"> b</td> </tr> </tbody> </table>
Verwendung des VBA-Makros
Die Tabelle muss im Excel-Tabellenblatt ausgewählt werden. Anschließend wird das Makro gestartet, ein Dateiname und der Speicherpfad gewählt und der Tabelleninhalt wird inklusive aller oben genannten Formatierungen als HTML- und CSS-Code in die Datei geschrieben.
Die Datei enthält reinen ASCII-Code, ist also eine reine Text-Datei. Mit einem beliebigen Texteditor kann die Datei geöffnet werden und der Inhalt komplett in die Zwischenablage kopiert werden.
Aus der Zwischenablage kann der Code dann in den Ziel-HTML-Code eingefügt werden – fertig.
Hinweis:
Der Code funktioniert nur in HTML5-Seiten. Im Code wird ein lokales Stile-Sheet erzeugt, welches innerhalb des HTML-Körpers (Body) abgelegt wird. Das ist erst ab HTML5 erlaubt und wird in Browsern nur in HTML5-codierten Seiten unterstützt.
Vorgehensweise – die Teilschritte und deren Umsetzung in VBA-Code
Ermittlung von Größe und Inhalt der Tabelle
- erste und letzte Spalte und Zeile als Zahl ermitteln (für Adressierung mit cell(…))
- Anzahl sichtbarer Spalten ermitteln
Dim iFirstRow, iFirstCol, iLastRow, iLastCol, iColCount As Integer
Dim strAdresse() As String
...
strAdresse = Split(Selection.Address, "$")
iFirstCol = Range(strAdresse(1) & "1").Column
iFirstRow = Val(strAdresse(2))
iLastRow = Selection.Cells(Selection.Cells.Count).Row
iLastCol = Selection.Cells(Selection.Cells.Count).Column
iColCount = 0
For iCnt2 = iFirstCol To iLastCol
' Anzahl Spalten ...
If Columns(iCnt2).Hidden <> True Then
iColCount = iColCount + 1
End If
Next iCnt2
- Wenn erste und letzte Spalte / Zeile nicht benötigt würde, könnte man die Spaltenanzahl auch wie folgt ermitteln:
Dim col As Range
iColCount = 0
For Each col In Selection.Columns
If Columns.Hidden <> True Then
iColCount = iColCount + 1
End If
Next
- prüfen, ob es Zellen mit Inhalt gibt
…hier ein Code-Schnippsel:
Dim rngCell As Range
...
bFlag = False
For Each rngCell In Selection
If rngCell.Value <> "" Then
bFlag = True
Exit For
End If
Next
Tabellen-Layout ermitteln
Für die spätere Verarbeitung wird das Tabellen-Layout in VBA-Arrays abgelegt. Die Arrays sind als „Integer“ deklariert. Um Speicherplatz zu sparen, könnten sie auch als „Byte-Arrays“ deklariert werden.
Laufvariablen und „Merker“ für Zeilen und Spalten wurden bewusst als „Integer“ vereinbart, da es ohnehin keinen Sinn ergibt, derart riesige Tabellen als HTML-Code zu erzeugen.
- verbundene Zellen suchen und merken …
For iRowCnt = iFirstRow To iLastRow
' ausgeblendete Zeilen auslassen ...
If Rows(iRowCnt).Hidden <> True Then
For iColCnt = iFirstCol To iLastCol
' ausgeblendete Spalten auslassen ...
If Columns(iColCnt).Hidden <> True Then
iTableLayout(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = 0
If Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt).MergeCells Then
' 1 in iTableLayout(zeile, spalte) bedeutet verbundene Zelle
iTableLayout(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = 1
strAdresse = Split(Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt).MergeArea.Address(), "$")
iFirstMergedCol = Range(strAdresse(1) & "1").Column
iFirstMergedRow = Val(strAdresse(2))
iLastMergedCol = Range(strAdresse(3) & "1").Column
iLastMergedRow = Val(strAdresse(4))
If iFirstMergedCol <> iLastMergedCol Then
' verbundene Zellen spaltenweise erfassen; Anzahl merken
iColSpan(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iLastMergedCol - iFirstMergedCol + 1
End If
If iFirstMergedRow <> iLastMergedRow Then
' verbundene Zellen zeilenweise erfassen; Anzahl merken
iRowSpan(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iLastMergedRow - iFirstMergedRow + 1
End If
End If 'Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt).MergeCells
End If 'Columns(iColCnt).Hidden <> True
Next iColCnt
End If 'Rows(iRowCnt).Hidden <> True
Next iRowCnt
colspan-Werte fürtd-Elemente bilden
For iCntR = 0 To iLastRow - iFirstRow
For iCntC = 0 To iLastCol - iFirstCol
If iColSpan(iCntR, iCntC) = 0 Then
iTdCol(iCntR, iCntC) = 1
Else
iTdCol(iCntR, iCntC) = iColSpan(iCntR, iCntC)
ihVar = iColSpan(iCntR, iCntC)
For ihVar2 = 1 To ihVar - 1
iTdCol(iCntR, iCntC + ihVar2) = 0
Next ihVar2
iCntC = iCntC + ihVar - 1
End If
Next iCntC
Next iCntR
rowspan-Werte fürtd-Elemente bilden
For iCntC = 0 To iLastCol - iFirstCol
For iCntR = 0 To iLastRow - iFirstRow
If iRowSpan(iCntR, iCntC) = 0 Then
iTdRow(iCntR, iCntC) = 1
Else
iTdRow(iCntR, iCntC) = iRowSpan(iCntR, iCntC)
ihVar = iRowSpan(iCntR, iCntC)
For ihVar2 = 1 To ihVar - 1
iTdRow(iCntR + ihVar2, iCntC) = 0
Next ihVar2
iCntR = iCntR + ihVar - 1
End If
Next iCntR
Next iCntC
Wenn in beiden Arrays, iTdRow und iTdCol ein Wert verschieden von Null steht, wird ein td-Element erzeugt.
- Formatierung der Tabellen-Zellen ermitteln; die Formatierung wird anschließend über CSS-Klassen definiert
- es werden zwei CSS-Klassen gebildet
- eine für die Rahmen-Eigenschaften
border - die andere für
background-color,text-decoration,font-style,font-weight,font-size,font-size font-style,font-weight,font-size,font-typewerden zunächst global ermittelt und nur dann für die einzelnen Tabellenzellen in Style-Sheet übernommen, wenn sie sich von den globalen unterscheiden
'** Zellenformate ermitteln ...
'**
For iRowCnt = iFirstRow To iLastRow
' ausgeblendete Zeilen auslassen ...
If Rows(iRowCnt).Hidden <> True Then
For iColCnt = iFirstCol To iLastCol
' ausgeblendete Spalten auslassen ...
If Columns(iColCnt).Hidden <> True Then
Call GetRangeFormatInfo(Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt), usrFormatInfo)
' Zeilenhoehe merken ...
iTrRowHeight(iRowCnt - iFirstRow) = usrFormatInfo.iRangePixelHeight
' Rahmenformatierung ermitteln
strBorderFormat(iCSSborderCnt) = _
"border-color: " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vTop, 6) & " " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vRight, 6) & " " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vBottom, 6) & " " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vLeft, 6) & ";" & strCrLf & _
"border-style: " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vTop) & " " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vRight) & " " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vBottom) & " " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vLeft) & ";" & strCrLf & _
"border-width: " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vTop & "px " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vRight & "px " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vBottom & "px " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vLeft & "px;" & strCrLf
If iCSSborderCnt > 0 Then
bCSSstyleFound = False
For iCSSrunVar = 0 To iCSSborderLastIdx
If iCSSrunVar <> iCSSborderCnt Then
If strBorderFormat(iCSSrunVar) = strBorderFormat(iCSSborderCnt) Then
bCSSstyleFound = True
' Format fuer Zelle merken ...
iColSpan(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iCSSrunVar
Exit For
End If
End If
Next iCSSrunVar
If bCSSstyleFound = False Then ' Stile war noch nicht vorhanden
' Format fuer Zelle merken ...
iColSpan(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iCSSborderCnt
iCSSborderCnt = iCSSborderCnt + 1
iCSSborderLastIdx = iCSSborderCnt
End If
Else
' Format fuer Zelle merken ...
iColSpan(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iCSSborderCnt
iCSSborderCnt = iCSSborderCnt + 1
iCSSborderLastIdx = iCSSborderCnt
End If
strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) = _
"color: #" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.lFontColor, 6) & ";" & strCrLf & _
"background-color: #" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.lInteriorColor, 6) & ";" & strCrLf & _
"text-decoration: " & usrFormatInfo.vTextDecoration & ";" & strCrLf
' "font-style: " & GetFontStyle(usrFormatInfo.bFontItalic) & ";" & strCrLf & _
' "font-weight: " & GetFontWeight(usrFormatInfo.bFontBold) & ";" & strCrLf & _
' "font-size: " & Round(usrFormatInfo.vFontSize * vScreenRes / 72) & "px;" & strCrLf & _
' "font-size: " & usrFormatInfo.vFontName & ";" & strCrLf
If strFontStyleGlobal <> GetFontStyle(usrFormatInfo.bFontItalic) Then
strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) = strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) & _
"font-style: " & GetFontStyle(usrFormatInfo.bFontItalic) & ";" & strCrLf
End If
If strFontWeightGlobal <> GetFontWeight(usrFormatInfo.bFontBold) Then
strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) = strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) & _
"font-weight: " & GetFontWeight(usrFormatInfo.bFontBold) & ";" & strCrLf
End If
If vFontSizeGlobal <> usrFormatInfo.vFontSize Then
strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) = strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) & _
"font-size: " & Round(usrFormatInfo.vFontSize * vScreenRes / 72) & "px;" & strCrLf
End If
If strFontNameGlobal <> usrFormatInfo.vFontName Then
strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) = strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) & _
"font-family: " & usrFormatInfo.vFontName & ";" & strCrLf
End If
' Zentrierung ...
Call CheckCellHorizontalAlignment(Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt), strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt))
Call CheckCellVerticalAlignment(Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt), strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt))
If iCSSformatCnt > 0 Then
bCSSstyleFound = False
For iCSSrunVar = 0 To iCSSformatLastIdx
If iCSSrunVar <> iCSSformatCnt Then
If strCellFormat(iCSSrunVar) = strCellFormat(iCSSformatCnt) Then
bCSSstyleFound = True
' Format fuer Zelle merken ...
iTableLayout(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iCSSrunVar
Exit For
End If
End If
Next iCSSrunVar
If bCSSstyleFound = False Then ' Stile war noch nicht vorhanden
' Format fuer Zelle merken ...
iTableLayout(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iCSSformatCnt
iCSSformatCnt = iCSSformatCnt + 1
iCSSformatLastIdx = iCSSformatCnt
End If
Else
' Format fuer Zelle merken ...
iTableLayout(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) = iCSSformatCnt
iCSSformatCnt = iCSSformatCnt + 1
iCSSformatLastIdx = iCSSformatCnt
End If
End If 'Columns(iColCnt).Hidden <> True
Next iColCnt
End If
Next iRowCnt
Tabellen-Zellen mit gleicher Formatierung erhalten die gleiche CSS-Klasse. Damit wird wesentlich die Länge des erzeugten Codes beeinflusst. Je mehr unterschiedlich formatierte Zellen es gibt, desto größer wird die erzeugte ASCII-Datei mit dem HTML-Code.
HTML-Code für Tabelle erzeugen
- Lokales Style-Sheet mit den CSS-Klassen für die Zellenformatierung erzeugen und in Datei speichern
- Wenn mehrere mit diesem Makro generierte Tabellen in einer Webseite eingefügt werden, muss dafür gesorgt werden, dass es die CSS-Klassen für die Zell-Formatierung nur jeweils einmal gibt. Sonst kann es zu ungewollten Seiteneffekten kommen, die sich in falschen Darstellungen widerspiegeln.
- Um das zu gewährleisten, werden die CSS-Klassen-Namen so gebildet, dass Dopplungen unwahrscheinlich werden.
- Bildung der CSS-Klassen-Namen
' CSS-Klassennamen bilden ... Dim strCssClassName As String strCssClassName = "tdc" & Mid$(Replace(Date, ".", ""), 1, 2) & Mid$(Replace(Time, ":", ""), 3, 4)
- lokales Style-Sheet erzeugen; wird über das
style-Attribut mit dem Attributscopedin denbody-Bereich vor der Tabelle eingefügt
' Lokale Stylesheets fuer HTML erzeugen ...
strData = "<style scoped>" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
' gemeinsame Eigenschaften
strData = "td {" & strCrLf
strData = strData & _
"font-style: " & strFontStyleGlobal & ";" & strCrLf & _
"font-weight: " & strFontWeightGlobal & ";" & strCrLf & _
"font-size: " & Round(vFontSizeGlobal * vScreenRes / 72) & "px;" & strCrLf & _
"font-family: " & usrFormatInfo.vFontName & ";" & strCrLf & "}" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
' Rahmen ...
For iCSSrunVar = 0 To iCSSborderLastIdx - 1
strData = "td." & strCssClassName & "b-" & iCSSrunVar & " {" & strCrLf
strData = strData & strBorderFormat(iCSSrunVar) & strCrLf & "}" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
Next iCSSrunVar
' font-style, font-weight, font-size, font-size
For iCSSrunVar = 0 To iCSSformatLastIdx - 1
strData = "td." & strCssClassName & "-" & iCSSrunVar & " {" & strCrLf
strData = strData & strCellFormat(iCSSrunVar) & strCrLf & "}" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
Next iCSSrunVar
strData = "</style>" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
- Tabellenkopf erzeugen; wesentliche Formatierungen werde über inline-style im table-Element eingefügt
- wichtige Einstellungen für die Darstellung der Tabelle sind:
text-align: inherit;,vertical-align: inherit;,border-collapse: collapse;,border-spacing: 0;,width: inherit;
Call GetRangeFormatInfo(rngBereich, usrFormatInfo)
' Tabellenkopf ... HTML5
strData = "<table style=" & Chr(34) & _
"text-align: inherit; " & "vertical-align: inherit;" & "border-collapse: collapse;" & "border-spacing: 0;" & "width: inherit;" & _
"border-color: " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vTop, 6) & " " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vRight, 6) & " " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vBottom, 6) & " " & _
"#" & Application.WorksheetFunction.Dec2Hex(usrFormatInfo.vBorderColor.vLeft, 6) & ";" & strCrLf & _
"border-style: " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vTop) & " " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vRight) & " " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vBottom) & " " & _
GetLineStyle(usrFormatInfo.vBorderLineStyle.vLeft) & ";" & strCrLf & _
"border-width: " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vTop & "px " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vRight & "px " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vBottom & "px " & _
usrFormatInfo.vBorderWeight.vLeft & "px;" & strCrLf & _
Chr(34) & ">" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
- Spaltenbreiten aus Excel übernehmen und in HTML codieren
strData = "<colgroup>" & strCrLf
For iColCnt = iFirstCol To iLastCol
' ausgeblendete Spalten auslassen ...
If Columns(iColCnt).Hidden <> True Then
ihVar = GetCellPixelWidth(Cells(1, iColCnt), 96)
strData = strData & "<col width=" & Chr(34) & ihVar & Chr(34) & ">" & strCrLf
End If
Next iColCnt
strData = strData & "</colgroup>" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData
- Tabellenkörper schreiben; ein
td-Element wird nur erzeugt. wenn in beiden Arrays,iTdRowundiTdColein Wert verschieden von Null steht - im Zelleninhalt werden Zeilenumbrüche durch das HTML-Token
<br />
strData = "<tbody>" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
' Tabellenbildung
For iRowCnt = iFirstRow To iLastRow 'ActiveSheet.Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeLastCell).Row
' ausgeblendete Zeilen auslassen ...
If Rows(iRowCnt).Hidden <> True Then
' Zeile einleiten ...
strData = "<tr " & _
" style=" & Chr(34) & _
"height: " & iTrRowHeight(iRowCnt - iFirstRow) & "px;" & Chr(34) & ">" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
For iColCnt = iFirstCol To iLastCol
' ausgeblendete Spalten auslassen ...
If Columns(iColCnt).Hidden <> True Then
If iTdCol(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) * iTdRow(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) > 0 Then
strData = "<td " & "class=" & Chr(34) & strCssClassName & "-" & iTableLayout(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) & _
" " & strCssClassName & "b-" & iColSpan(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) & _
Chr(34) & " colspan=" & Chr(34) & iTdCol(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) & Chr(34) & _
" rowspan=" & Chr(34) & iTdRow(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) & Chr(34)
strData = strData & ">" & strCrLf
strData = strData & Replace(Trim(Cells(iRowCnt, iColCnt).Text), vbLf, "<br />")
strData = strData & "</td>" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
End If 'iTdCol(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) * iTdRow(iRowCnt - iFirstRow, iColCnt - iFirstCol) > 0
End If 'Columns(iColCnt).Hidden <> True
Next iColCnt
strData = "</tr>" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
End If
Next iRowCnt
strData = "</tbody>" & strCrLf & "</table>" & strCrLf
Print #filenr, strData;
…wird fortgesetzt.
Weiter zu Teil2.
